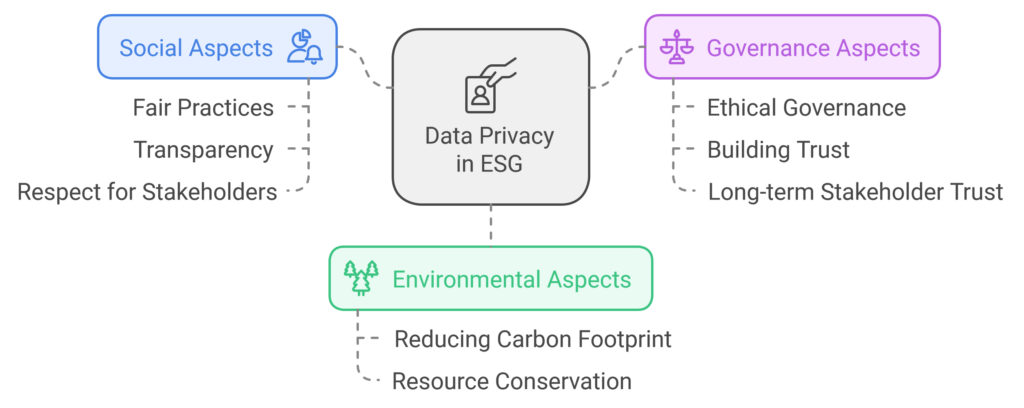
In the digital age, data has become one of the most valuable assets for organizations. However, with this value comes a great responsibility to handle personal and sensitive information with care. Data privacy is now more than just a legal obligation—it’s a fundamental part of how businesses show respect for individual rights and build trust with customers. Within the framework of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles, data privacy has taken a central role, particularly in the Social and Governance components.
The Role of Data Privacy in ESG
ESG, originally a tool for evaluating corporate performance based on broader social and environmental impact, has evolved to encompass critical components of digital responsibility. While many businesses focus on the Environmental aspects of ESG, such as reducing carbon footprints or conserving resources, the Social and Governance aspects are just as crucial. Data privacy policies fall under both, as they pertain to a company’s commitment to fair practices, transparency, and respect for stakeholders.
By prioritizing data privacy, companies can demonstrate their commitment to ethical governance and social responsibility, building a solid foundation for long-term trust with their stakeholders.
Why Strong Data Privacy Policies Are Important
Here’s why strong data privacy policies are essential for ESG compliance:
1. Building Trust and Reputation
Data breaches and mishandling of personal information can severely damage a company’s reputation, eroding public trust. In an era where customers are increasingly aware of their digital rights, a strong data privacy policy reflects a company’s commitment to transparency and ethical behavior. This is a positive indicator for investors who prioritize ESG, as trustworthiness is key to sustainable business growth.
2. Meeting Regulatory Standards
Governments worldwide are implementing stringent data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions, and it can impact a company’s ESG rating. Adhering to these regulations shows that a company respects the rights of individuals, a core component of the Social and Governance aspects of ESG.
3. Risk Management and Security
In an age of increased cybersecurity threats, poor data privacy policies can expose companies to data breaches, hacks, and other cybercrimes. Robust data privacy policies are proactive risk management tools. For ESG-conscious investors, a company’s data privacy approach is a significant indicator of its risk preparedness, resilience, and commitment to long-term value protection.
4. Respecting Customer Privacy and Social Responsibility
Data privacy policies are a way for companies to respect their customers’ personal information, reflecting a larger commitment to social responsibility. As companies collect vast amounts of data to analyze trends, improve products, or personalize services, they need to do so in ways that respect individual privacy. Protecting this data aligns with a company’s obligation to treat all stakeholders—customers, employees, and communities—with respect.
5. Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
Strong data privacy policies enhance transparency by clearly communicating how data is collected, used, shared, and stored. This aligns with the Governance pillar of ESG by promoting a culture of accountability within organizations. When a company adopts strong privacy practices, it shows it’s willing to be held accountable for how it handles data, building trust with its stakeholders.
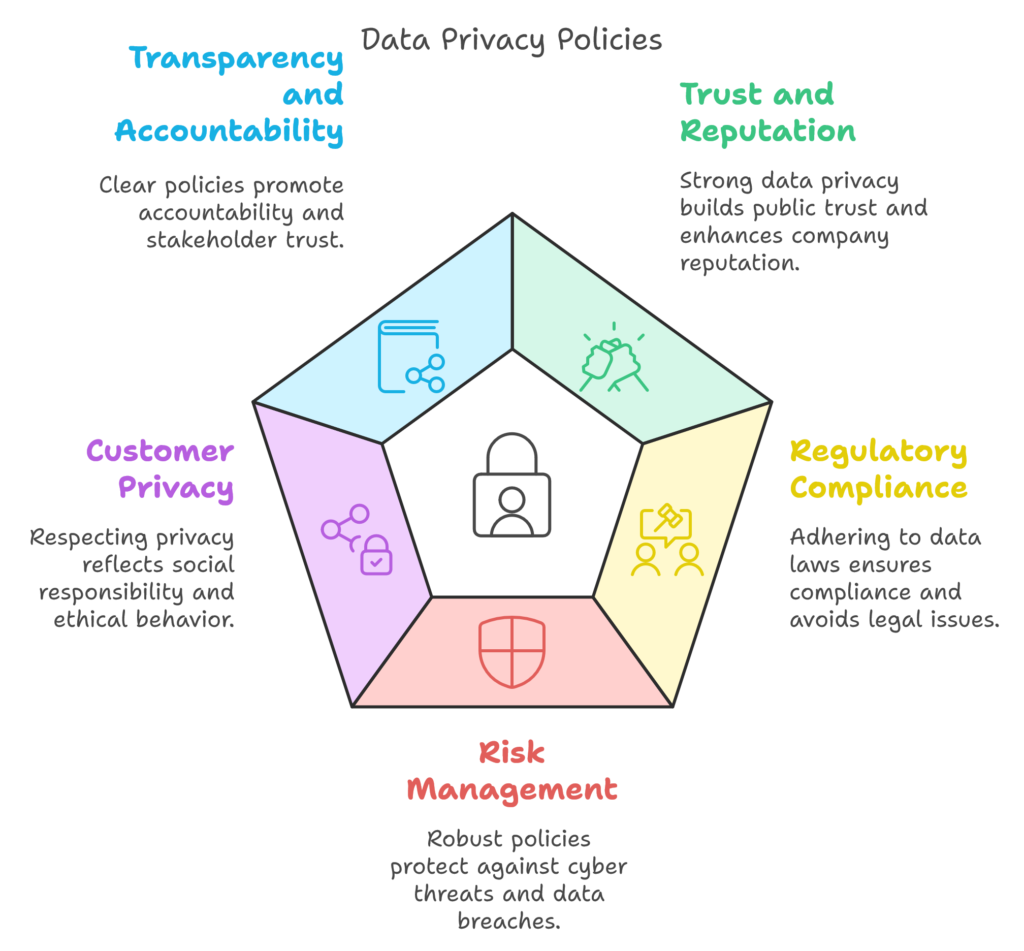
Key Elements of Strong Data Privacy Policies for ESG
A strong data privacy policy that aligns with ESG should include several key elements:
- Clear Data Collection Policies: Transparency on data collection practices, ensuring users know what data is collected and why.
- Consent and Choice: Offering users control over their data and providing them with clear options for consent and data sharing.
- Data Minimization: Collecting only the data necessary for business needs and protecting it accordingly.
- Robust Security Measures: Implementing strong security practices, like encryption and secure storage, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Data Deletion and Retention Policies: Defining clear timelines for data retention and deletion to avoid unnecessary storage of personal information.
- Incident Response Plans: Ensuring quick, transparent action in case of a data breach, including notification procedures and damage mitigation.
The Business Benefits of Strong Data Privacy Policies
In addition to ESG compliance, there are several business advantages to maintaining strong data privacy policies:
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with solid data privacy practices are more appealing to ESG-conscious investors, giving them a competitive edge in attracting investment and customers.
- Customer Loyalty: Strong privacy practices can foster customer loyalty, as clients are more likely to trust companies that respect their privacy.
- Innovation and Efficiency: Privacy-enhancing technologies, such as data anonymization or tokenization, encourage innovation and allow companies to process data in secure and ethical ways.
- Better Compliance with International Standards: Adopting strong privacy practices prepares companies for international expansion by ensuring they can comply with global privacy laws.
Case Studies: Companies Leading in Data Privacy and ESG
Some companies are setting examples in data privacy by incorporating robust policies into their ESG practices:
- Apple: Apple has integrated data privacy as a core aspect of its product design, emphasizing transparency and user control over data. Its focus on privacy as a fundamental human right aligns with its social responsibility and governance commitments under ESG.
- Microsoft: Microsoft invests heavily in cybersecurity and privacy, creating user-friendly tools that enhance transparency and control over data. Its compliance with GDPR and other global regulations reflects its commitment to governance.
- Salesforce: As a company that relies heavily on customer data, Salesforce incorporates privacy as part of its social responsibility within ESG. It provides customers with tools for data management, reinforcing transparency and control over personal data.
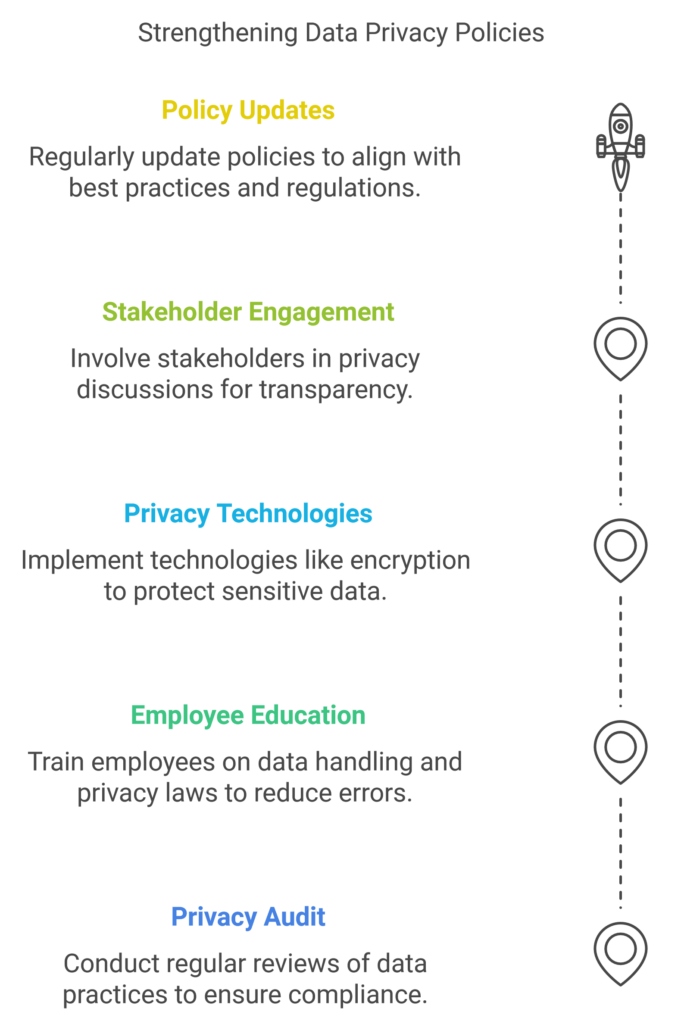
Practical Steps to Strengthen Data Privacy Policies for ESG Compliance
Here are some steps businesses can take to strengthen their data privacy policies and align them with ESG principles:
- Conduct a Privacy Audit: Regularly review data collection, storage, and processing practices to ensure compliance with current laws and regulations.
- Educate Employees on Data Privacy: Provide regular training to employees on data handling, security practices, and privacy laws to minimize human error.
- Invest in Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Implement encryption, access control, and other technologies to protect sensitive data.
- Engage Stakeholders: Actively involve customers, employees, and partners in privacy discussions to create a transparent and inclusive approach to data privacy.
- Regularly Review and Update Policies: Data privacy is an evolving field; regular policy updates ensure continued alignment with best practices and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
In today’s data-driven world, privacy has become an essential component of ESG compliance. Companies that establish strong data privacy policies not only protect their customers’ rights but also build trust, manage risks, and uphold high standards of transparency and accountability. As stakeholders place more importance on ethical data practices, strong data privacy policies are becoming indispensable for companies aiming to succeed in the ESG landscape. By prioritizing data privacy, companies are not only adhering to regulations but also demonstrating their commitment to a responsible, future-focused approach to business.