The rising emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles is driving businesses and communities toward more sustainable practices. One of the key areas of focus has been green building initiatives, which are designed to minimize environmental impact, promote healthier indoor environments, and encourage responsible resource usage. As ESG becomes increasingly central to corporate responsibility, green building initiatives offer a powerful way for organizations to align with these values.
In this blog, we’ll explore how green buildings support ESG goals and why investing in sustainable infrastructure is a smart move for companies committed to sustainability, community well-being, and transparency.
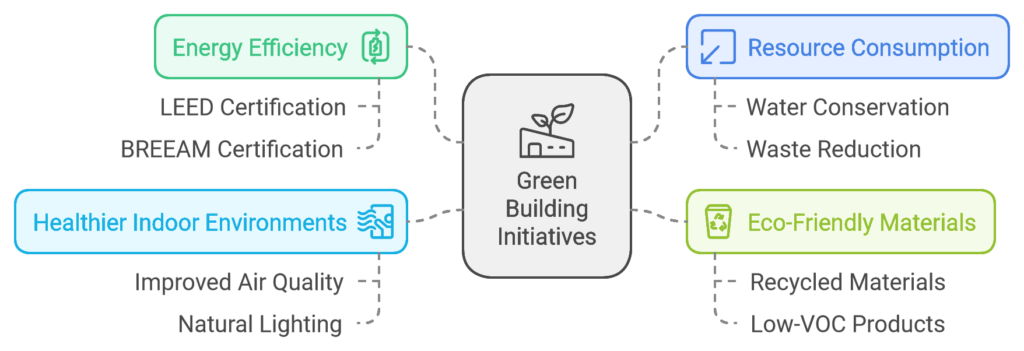
What Are Green Building Initiatives?
Green building initiatives refer to the design, construction, and operation of buildings with sustainability in mind. This encompasses a range of practices aimed at improving energy efficiency, reducing resource consumption, using eco-friendly materials, and creating healthier indoor environments. Organizations pursuing green building strategies often aim for certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), which validate sustainable building practices.
Aligning Green Building with ESG: Key Benefits and Strategies
1. Environmental Impact: Reducing Carbon Footprint and Resource Consumption
Green building initiatives directly contribute to the environmental component of ESG by prioritizing low-carbon and eco-friendly construction methods. From energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems to sustainable building materials, every aspect of green building aims to minimize the environmental footprint.
- Energy Efficiency: Using high-efficiency lighting, HVAC systems, and smart building technologies can reduce a building’s energy consumption by up to 50%. Solar panels and green roofs help generate renewable energy, further reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Water Conservation: Green buildings often incorporate water-saving technologies, such as low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems, which contribute to water conservation and reduced utility costs.
- Sustainable Materials: By using recyclable and responsibly sourced materials, green building practices lower the demand for natural resources and reduce construction waste. For instance, recycled steel, bamboo flooring, and non-toxic paints are becoming popular options.
Green building reduces greenhouse gas emissions, conserves resources, and aligns with the commitment to combat climate change—key objectives for companies pursuing strong ESG scores.
2. Social Responsibility: Promoting Healthier, Productive Spaces
Green buildings support the social aspect of ESG by creating healthy and comfortable environments for occupants. A better indoor climate can lead to increased productivity, improved employee satisfaction, and healthier workplaces, particularly important in regions where people spend most of their time indoors.
- Improved Air Quality: Green buildings focus on indoor air quality by utilizing natural ventilation, air purifiers, and low-emission materials. Improved air quality helps reduce respiratory issues, particularly important for urban areas with high pollution.
- Natural Lighting and Biophilic Design: Incorporating natural light and green spaces inside buildings is proven to boost mood, reduce stress, and enhance focus. Green spaces also encourage occupants to connect with nature, positively impacting mental health and productivity.
- Thermal Comfort: By using smart climate control systems, green buildings can ensure optimal temperatures, reducing the need for heating or cooling. This not only saves energy but also keeps employees comfortable throughout the day.
By prioritizing occupant well-being, green building initiatives reflect a company’s commitment to social responsibility, which is increasingly important to employees, tenants, and the communities they serve.
3. Governance: Transparency, Accountability, and Compliance
Green building initiatives often require adherence to specific certifications and regulations, promoting greater accountability and transparency—key elements of good governance in ESG. By meeting regulatory requirements and adopting industry standards, companies demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
- Certification and Benchmarking: Certifications like LEED and BREEAM provide standardized benchmarks, offering an objective measure of a building’s environmental impact. Achieving and maintaining these certifications requires transparent reporting, which helps build trust with stakeholders.
- Sustainable Practices in Operations: Governance around sustainable building involves monitoring and maintaining efficiency standards, waste management, and energy audits. These governance practices help companies meet both regulatory and stakeholder expectations.
- Data Collection and Reporting: Many green buildings are equipped with advanced systems for monitoring energy usage, water consumption, and other sustainability metrics. Transparent reporting of these metrics helps maintain ESG compliance, which is essential as regulatory bodies and investors increasingly demand ESG disclosures.
Governance in green building helps ensure that sustainable practices are maintained over the long term, holding organizations accountable for their environmental and social impacts.
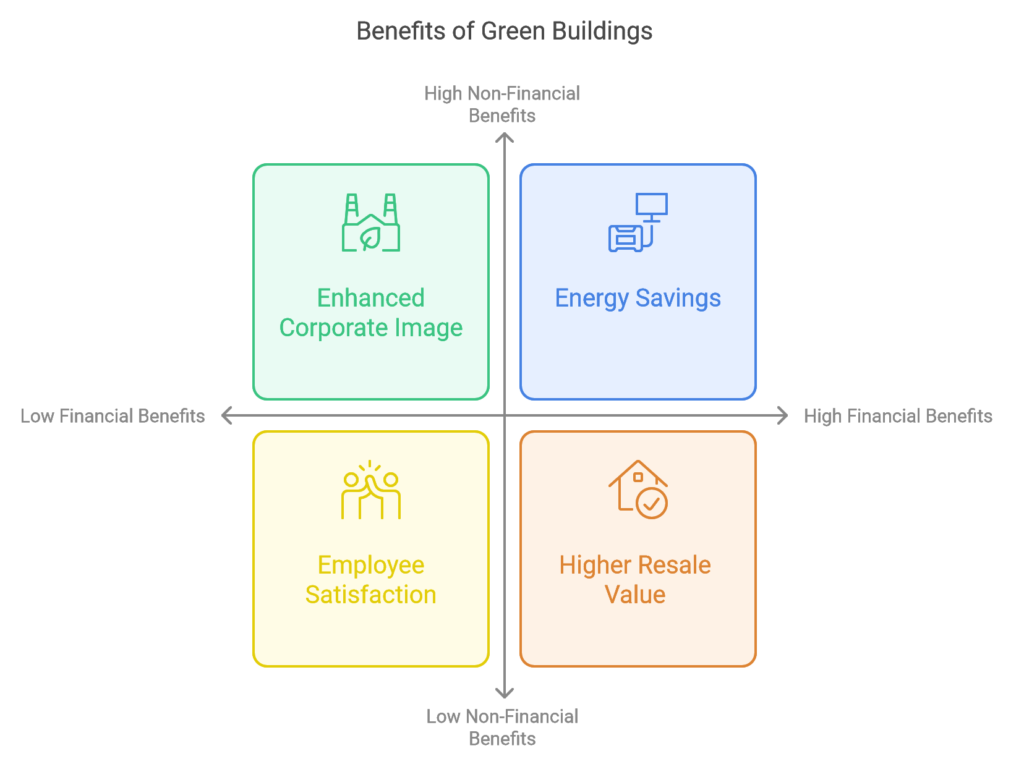
Why Green Buildings Are Good for Business
Cost Savings and Long-Term Investment
While the initial costs of green buildings may be higher than traditional construction, the long-term financial benefits make it a worthwhile investment. Energy-efficient buildings can yield significant savings on utility bills, and with the rising costs of resources like water and electricity, these savings are likely to grow. Additionally, green buildings often have higher resale values, making them attractive assets in the long term.
Enhanced Corporate Image and Competitive Advantage
Green building initiatives enhance a company’s brand by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility. As consumers and investors become more aware of the importance of ESG, companies with strong sustainability practices are seen as industry leaders and enjoy better reputational standing. For businesses aiming to attract ESG-conscious investors, employees, or clients, investing in green buildings can set them apart from competitors.
Employee Retention and Productivity
Green buildings are also beneficial for employee morale and retention. Employees tend to be more satisfied and productive in healthier, environmentally-friendly workspaces. By investing in green building initiatives, companies can show employees that their health and well-being are priorities, improving both retention and productivity rates.
Examples of Green Building Practices in ESG-Aligned Companies
1. Google’s Bay View Campus (California, USA)
Google’s Bay View campus is one of the world’s largest net-zero water and net-zero carbon buildings, designed to run on 100% renewable energy. The campus includes sustainable features like photovoltaic panels, geothermal wells, and an onsite wastewater treatment system, supporting Google’s commitment to environmental goals.
2. Unilever’s Energy-Efficient Offices (London, UK)
Unilever’s headquarters in London is an example of sustainable architecture, using recycled materials, energy-efficient systems, and green spaces to reduce its environmental footprint. The building also prioritizes employee well-being with ample natural light, ventilation, and green spaces.
3. Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) Global Offices
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) has incorporated green building practices in its offices across India, integrating energy-saving technologies and water recycling systems. TCS has received multiple LEED certifications for its commitment to sustainability in its operations, demonstrating its dedication to reducing its environmental impact.
Conclusion: Why Green Building Initiatives Are Essential for ESG Goals
As ESG principles become essential components of corporate responsibility, green building initiatives offer a tangible way for organizations to address environmental and social goals. Through energy-efficient design, health-focused indoor environments, and transparent governance, green buildings help businesses reduce their environmental footprint, improve workplace satisfaction, and meet evolving regulatory standards.
Investing in green building practices is not only beneficial for the planet but also provides long-term value for companies. As stakeholders, employees, and consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability, green buildings will continue to play a vital role in aligning business practices with ESG objectives. For companies committed to future-proofing their operations, adopting green building practices is a significant step toward sustainable growth and meaningful impact.