Water is one of Earth’s most valuable resources, essential not only for human life but for ecosystems and businesses across every industry. As water scarcity grows due to climate change, over-extraction, and population increases, conserving water has become a top priority for companies and investors committed to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles.
Integrating water conservation into ESG strategies is about more than reducing costs—it’s about protecting natural resources, supporting communities, and preparing for a sustainable future. In this blog, we’ll explore why water conservation is essential for ESG, key water-saving practices for companies, and how investors can encourage sustainable water management.
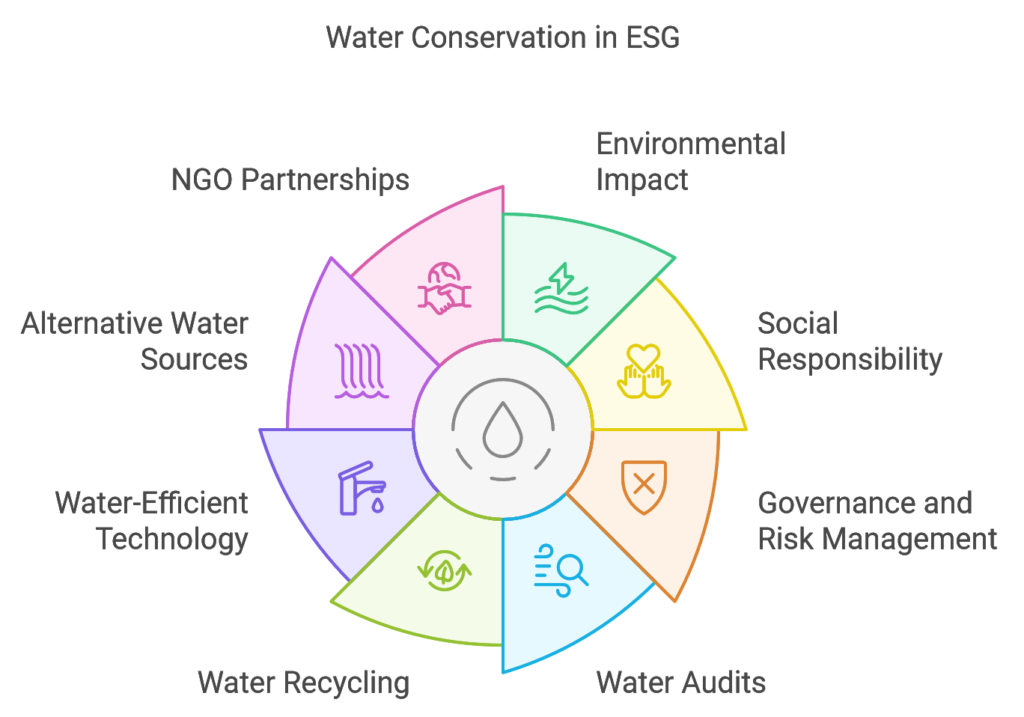
The Importance of Water Conservation in ESG
Water is integral to numerous aspects of a company’s ESG profile, affecting environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. Here’s how water conservation ties into each component of ESG:
1. Environmental Impact
Water scarcity is one of the most pressing environmental issues today, with global freshwater demand expected to outpace supply by 2030. Industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and energy consume massive quantities of water, which strains local ecosystems and depletes natural water sources. Companies that prioritize water conservation help reduce this strain, protect ecosystems, and lower their overall environmental footprint.
2. Social Responsibility
Access to clean water is a basic human right, yet millions worldwide face water scarcity or inadequate sanitation. Companies that actively manage their water usage and minimize pollution contribute to the well-being of the communities in which they operate. Socially responsible companies focus on water conservation practices that benefit both their operations and the communities they serve, improving quality of life and fostering positive relationships with local stakeholders.
3. Governance and Risk Management
Water-related risks are increasingly affecting businesses—from supply chain disruptions due to droughts to operational restrictions from stricter water regulations. By implementing strong water management practices, companies demonstrate effective governance and proactive risk management, which are valued by investors and stakeholders. Transparent reporting on water use and conservation efforts also reflects accountability, building trust and credibility.
Key Water Conservation Practices for Companies
Water conservation practices can vary depending on a company’s size, industry, and location, but the following strategies can be applied across sectors to reduce water use and improve sustainability:
1. Conducting Water Audits
A water audit is an assessment of a company’s water consumption, identifying areas where water is being used inefficiently or wasted. By conducting regular audits, companies can better understand their water footprint, set reduction targets, and measure progress over time.
- Example: By analyzing water usage across facilities, a beverage company could identify water-intensive processes in production and implement strategies to minimize water use, such as upgrading equipment or changing manufacturing practices.
2. Implementing Water Recycling and Reuse Systems
Water recycling systems capture and treat wastewater so it can be reused within operations. This practice reduces the need for fresh water and helps companies meet sustainability goals.
- Example: Manufacturing plants often implement “closed-loop” systems where water used for cooling or cleaning is filtered and recirculated instead of being discharged, reducing overall water demand.
3. Upgrading to Water-Efficient Technology
Investing in water-efficient technologies, such as low-flow fixtures, drip irrigation, or waterless cooling systems, can significantly reduce water usage in industrial and commercial settings.
- Example: Agriculture businesses can use drip irrigation, which directs water precisely to plants’ roots, reducing water use by up to 60% compared to traditional methods.
4. Using Alternative Water Sources
Companies can explore alternative water sources, like rainwater harvesting or using treated greywater (wastewater from sinks or showers) for non-potable purposes, such as landscape irrigation or industrial processes.
- Example: Some tech companies with large campuses collect rainwater for landscaping purposes, significantly reducing their reliance on municipal water supplies.
5. Partnering with NGOs and Local Communities
By collaborating with non-governmental organizations (NGOs), industry groups, and local communities, companies can identify water conservation solutions that benefit everyone. These partnerships help businesses understand local water issues and work with stakeholders to implement responsible water practices.
- Example: Beverage companies often work with NGOs to implement water conservation programs in water-stressed regions, helping replenish water sources and supporting local agriculture.
6. Reducing Pollution and Managing Wastewater
Proper treatment and disposal of wastewater are essential to preventing pollution. Companies that discharge untreated water into rivers or lakes harm the environment and face regulatory penalties. Implementing effective wastewater management systems not only conserves water but also protects ecosystems and communities from water contamination.
- Example: A mining company might invest in advanced filtration systems to treat water before it’s released into local waterways, reducing the risk of contamination.
Investor’s Role in Promoting Water Conservation
Investors play a crucial role in encouraging water conservation by supporting companies that prioritize sustainable water practices and by holding businesses accountable for their water usage. Here are some ways investors can promote water stewardship within their portfolios:
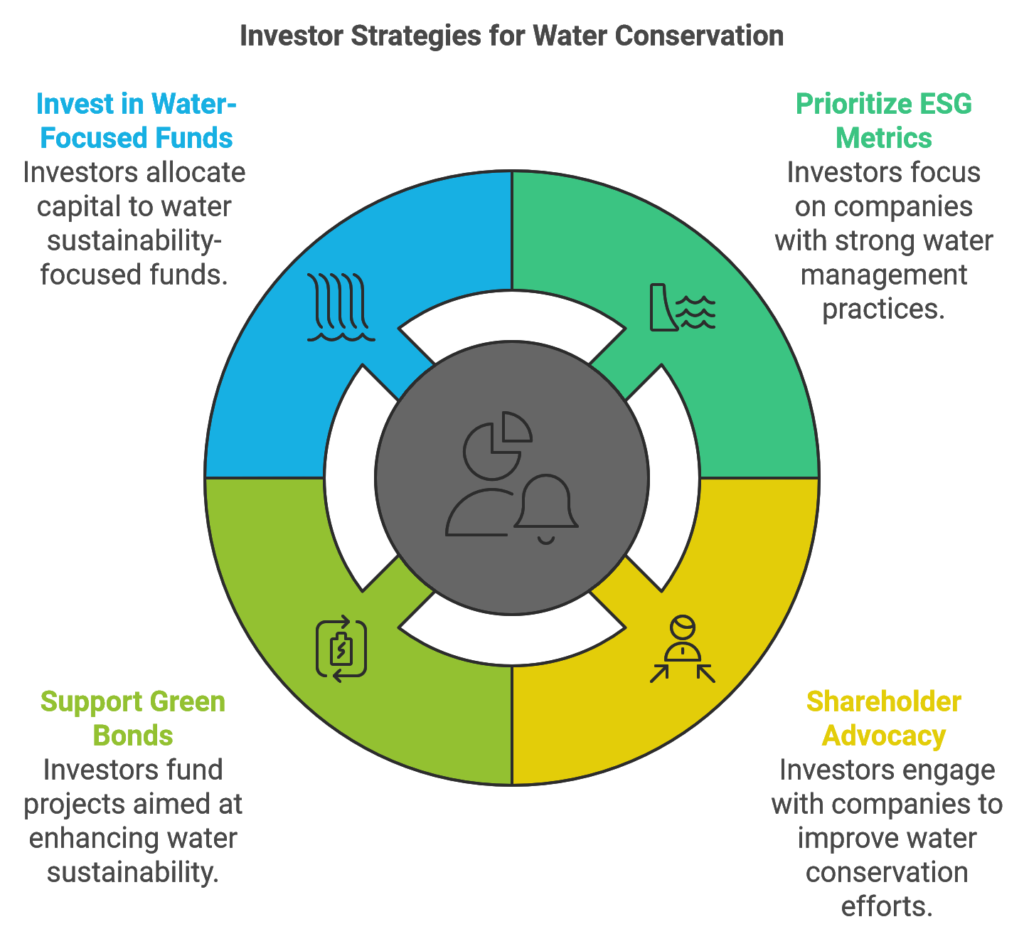
1. Prioritize ESG Metrics Related to Water Usage
When evaluating potential investments, investors can prioritize companies with strong water management practices. Look for companies with clear water conservation goals, transparent reporting on water use, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
- Example: ESG funds often screen companies based on water conservation metrics, including water usage per unit of production, water reuse rates, and wastewater treatment protocols.
2. Engage in Shareholder Advocacy
Investors can advocate for better water practices by engaging directly with companies through shareholder proposals, requesting transparency on water risks, and encouraging companies to set ambitious water conservation targets.
- Example: A group of investors could petition a large consumer goods company to disclose its water use in drought-prone areas and outline steps to reduce its water footprint.
3. Support Green Bonds for Water Conservation
Green bonds, designed to fund environmental projects, provide investors with a way to support companies and projects that focus on water conservation and management. Green bonds directed toward water sustainability projects offer financial returns and support global water conservation efforts.
- Example: Water-specific green bonds, such as those funding rainwater harvesting infrastructure or wastewater treatment facilities, allow investors to contribute to projects with measurable water conservation benefits.
4. Invest in Water-Focused Funds
Investors can allocate capital to funds that focus specifically on water sustainability, targeting companies in industries like water treatment, water technology, and sustainable agriculture. These funds help direct capital toward solutions that address global water challenges.
- Example: Water-focused ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) invest in companies involved in water technology, water infrastructure, and sustainable water management.
Conclusion: Water Conservation as a Core ESG Commitment
Water conservation is not only a crucial environmental goal but also an essential component of responsible corporate and investor practices. With the growing threat of water scarcity, companies that integrate water-saving measures into their operations are better positioned to mitigate risks, strengthen community relations, and improve long-term resilience.
For investors, supporting businesses that prioritize water conservation reflects a commitment to sustainable growth and responsible stewardship. By directing capital toward companies that actively reduce water use and address water-related risks, investors can contribute to a more sustainable and water-secure future.
As businesses and investors recognize the importance of water stewardship, they help create a more resilient economy that values and protects our planet’s precious resources—benefiting shareholders, stakeholders, and society as a whole.